[1] https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/child-maltreatment
[2]Stoltenborgh, M., Bakermans‐Kranenburg, M. J., Alink, L. R., & van IJzendoorn, M. H. (2015). The prevalence of child maltreatment across the globe: Review of a series of meta‐analyses. Child Abuse Review, 24(1), 37-50.
[3]UNICEF, R. (2012). Child maltreatment, prevalence, incidence and consequences in the East Asia and Pacific Region. New York: UNICEF.
[4]APSAC (1995). Psychosocial evaluation of suspected psychological maltreatment in children and adolescents. Practice Guidelines, American Professional Society on the Abuse of Children (1995).
[5]World Health Organization. (1999). Report of the Consultation on Child Abuse Prevention, 29–31 March 1999, WHO, Geneva. Geneva Switzerland: Author.
[6]Emotional abuse | NSPCC. (n.d.). Retrieved January 21, 2021, from https://www.nspcc.org.uk/what-is-child-abuse/types-of-abuse/emotional-abuse/
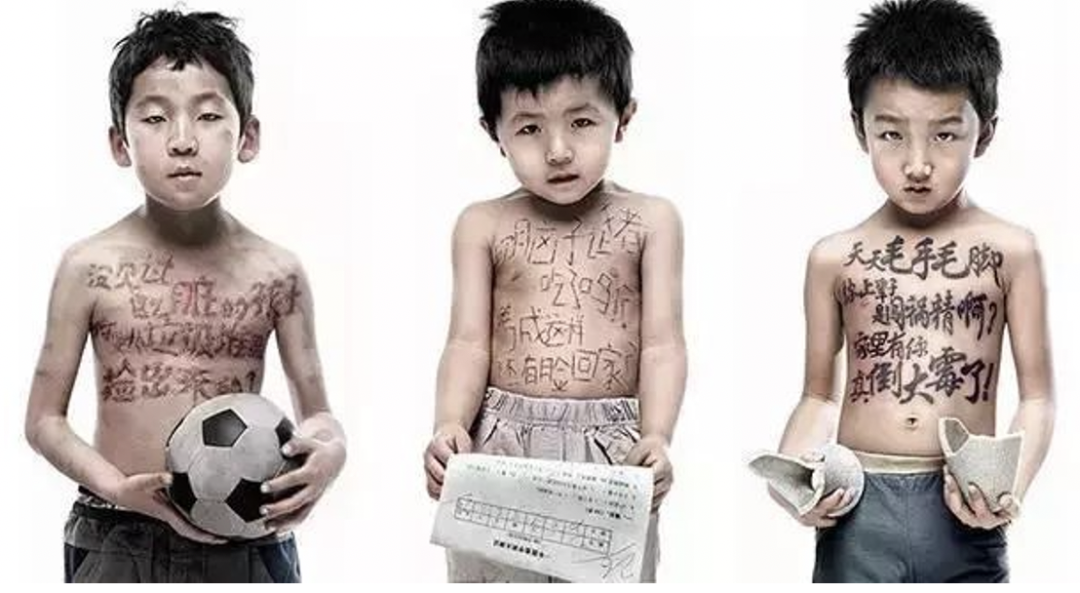
[7]有数 | 原生家庭之殇:从5243条数据看家庭语言暴力. (n.d.). Retrieved January 21, 2021, from https://m.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_8250520
[8]Carpenter, L. L., Tyrka, A. R., Ross, N. S., Khoury, L., Anderson, G. M., & Price, L. H. (2009). Effect of Childhood Emotional Abuse and Age on Cortisol Responsivity in Adulthood. Biological Psychiatry, 66(1), 69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.02.030
[9]Van Harmelen, A. L., Van Tol, M. J., Van Der Wee, N. J. A., Veltman, D. J., Aleman, A., Spinhoven, P., Van Buchem, M. A., Zitman, F. G., Penninx, B. W. J. H., & Elzinga, B. M. (2010). Reduced medial prefrontal cortex volume in adults reporting childhood emotional maltreatment. Biological Psychiatry, 68(9), 832–838.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.06.011
[10]Chen, C., & Qin, J. (2020). Emotional Abuse and Adolescents’ Social Anxiety: the Roles of Self-Esteem and Loneliness. Journal of Family Violence, 35(5), 497–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-019-00099-3
[11]Liu, S., Zhou, N., Dong, S., Wang, Z., & Hao, Y. (2019). Maternal childhood emotional abuse predicts Chinese infant behavior problems: Examining mediating and moderating processes. Child Abuse and Neglect, 88(23), 307–316.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2018.12.006
[12]Fang, X., Fry, D. A., Ji, K., Finkelhor, D., Chen, J., Lannen, P., & Dunne, M. P. (2015). The burden of child maltreatment in China: a systematic review. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 93(3), 176-185C. https://doi.org/10.2471/blt.14.140970
[13]Woudstra, M. J., Emmen, R. A. G., Alink, L. R. A., Wang, L., Branger, M. C. E., & Mesman, J. (2021). Attitudes about child maltreatment in China and the Netherlands. Child Abuse and Neglect, 112(April 2020), 104900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104900
[14]Chen, Y. lin, Liu, X., Huang, Y., Yu, H. jie, Yuan, S., Ye, Y. ling, Li, Q. xiao, & He, Q. qiang. (2017).Association between Child Abuse and Health Risk Behaviors among Chinese College Students. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26(5), 1380–1387.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0659-y
[15]Liao, M., Lee, A. S., Roberts-Lewis, A. C., Hong, J. S., & Jiao, K. (2011). Child maltreatment in China: An ecological review of the literature. Children and Youth Services Review, 33(9), 1709–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2011.04.031